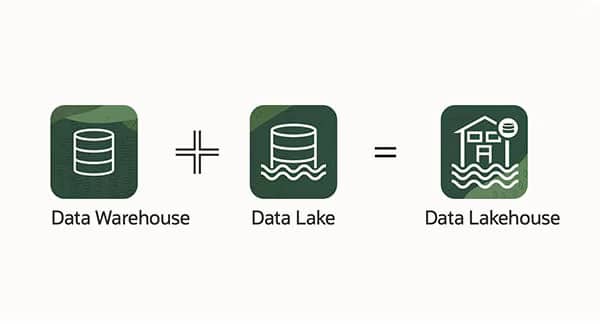
To optimize their data management and analysis, companies generally use two Data Science solutions: the data lake and the data warehouse. These two technologies offer numerous possibilities for data analysis and storage. However, a new system offers the possibility of merging the strengths of these two methods into a single software package, the data lakehouse.
In this article, discover the functionalities of this new approach and the advantages of integrating it into your business.
What is a data lakehouse?
A Data Lakehouse is a data architecture that aims to resolve the traditional shortcomings of data warehouses and data lakes. Unlike data warehouses, which are optimized for large-scale, structured queries, and data lakes, which are designed to store raw, unstructured data, the Data Lakehouse combines both approaches to provide a unified platform for data storage and analysis.
Thanks to the Data Lakehouse, companies can more easily exploit their data for Business Intelligence (BI) or Machine Learning (ML) purposes.
What are the differences between a data lake and a data warehouse?
The Data Warehouse :
A data warehouse functions like a central repository. Information comes from one or more data sources, such as a transactional system or other relational databases.
Data can be structured, semi-structured or unstructured. Once ingested into the Warehouse, it is processed and transformed. Users can then access it using Business Intelligence tools, SQL clients or spreadsheets.
By aggregating information in a single location, a company can benefit from an overview of its customer base or other crucial elements. Warehousing ensures that all information is reviewed.
The Data Warehouse also makes data mining possible. This involves searching for trends and patterns in the data, and building on them to increase sales and revenues.
The Data Lake:
A Data Lake can integrate data from different sources, such as databases, web servers or connected objects, using connectors. Data can be loaded in batches, or in real time.
The storage offered by a data lake is scalable, enabling rapid access for data mining. Once stored, data can be converted into a structured form to facilitate analysis. Data can be tagged to associate metadata.
SQL or NoSQL queries, or even Excel, can then be used to analyze the data. As soon as the company has a question, it is possible to run a query on the Data Lake, analyzing only a subset of the relevant data. The Data Lake also enables data management and governance.
The Data Lakehouse :
Data Lakehouses are based on an innovative design. It has data management structures and functions similar to those of a data warehouse, and is implemented directly in low-cost data lake storage.
Thanks to this fusion, teams can exploit data without having to access multiple systems, considerably speeding up their work. Another advantage of Data Lakehouses is that employees always have the most complete and up-to-date data for all their Data Science, Machine Learning and business analytics projects.
What does a data lakehouse consist of?
A data lake consists of two main layers. The lakehouse layer manages the storage of data in the data lake, so the processing layer can directly query the data in the storage using various tools without the data having to be loaded into a data warehouse or transformed into a proprietary format. The data can then be used by Business Intelligence applications or by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning tools.
This architecture offers the cost-efficiency of a data lake, enabling any type of processing engine to read this data. Organizations can then analyze the prepared data. In this way, processing and analysis can be carried out with better performance and at lower cost.
The architecture also enables multiple parties to simultaneously read and write data to the system, as it supports database transactions that respect the ACID principles (atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability):
- Atomicity means that when transactions are processed, either the entire transaction succeeds, or nothing succeeds. This prevents data loss or corruption in the event of a process interruption.
- Consistency ensures that transactions run predictably and logically. It ensures that all data is valid according to precise rules, maintaining data integrity.
- Isolation ensures that no transaction can be affected by another until it has been completed. This allows multiple parties to read and write to the same system without interfering with each other.
- Durability guarantees the persistence of changes made to data in a system after a transaction, even in the event of system failure. All modifications resulting from a transaction are stored permanently.

What are the advantages of a Data Lakehouse?
- Extreme flexibility: Data Lakehouses enable the storage of raw, semi-structured and structured data, without the need for predefined schemas. This offers exceptional flexibility for ingesting and exploring varied data, without the constraints of traditional data warehouses.
- Improved performance: unlike data lakes, data lakehouses incorporate indexing and query optimization capabilities, which significantly enhance analysis performance. Data can be processed faster, accelerating business insights.
- Data unification: Data Lakehouses eliminate data fragmentation by providing a focal point for storing and exploring diverse data sets. This promotes a holistic view of the enterprise, enabling users to access relevant information from a single platform.
- Informed decision-making: Thanks to the ability to store raw data and transform it into actionable information, companies can make more informed decisions based on hard data. Analyses can be carried out using real-time data, which is crucial in today’s business world.
- Scalability: Data Lakehouse architectures are designed to adapt to growing data storage and analysis needs. They can easily scale to handle massive amounts of data without compromising performance.

Now you know everything you need to know about data lakehouses, a new-generation data management and analysis solution that combines the flexibility of data lakes with the optimized performance of traditional data warehouses.
If you’ve enjoyed this article and are considering a career in data science and the development of next-generation algorithms, take a look at our training courses made by DataScientest.










