Artificial neural networks are at the core of the recent remarkable advancements in artificial intelligence. How do they function and what lends them their remarkable strength?
The mathematical concept of artificial neural networks (ANN) was first introduced in 1943 by two researchers from the University of Chicago, Warren McCullough, and Walter Pitts. In an article for the journal Brain Theory, they presented a theory that focused on the neuron as a fundamental element in responding to external stimuli.
It wasn’t until 1957 that the first prototype utilizing ANNs was developed—the Perceptron by Frank Rosenblatt. It aimed to perform recognition tasks using a repetitive learning algorithm. However, at the time, computers were not sufficiently powerful to process the vast amounts of data required for effective real-world application. This limitation was highlighted by Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert in their book Perceptrons (1969), where they pointed out the constraints of neural networks. Consequently, research in this area paused for nearly two decades.
A significant breakthrough occurred in 1986 when David Rumelhart, Geoffrey Hinton, and Ronald Williams published a paper on backpropagation, a learning technique that rekindled interest in neural networks.
However, it wasn’t until the advent of Big Data and massively parallel computers that neural networks received adequate processing power. A milestone was achieved in 2012 when Alex Krizhevsky’s team won the ImageNet competition, which focused on image recognition.

What is an artificial neural network?
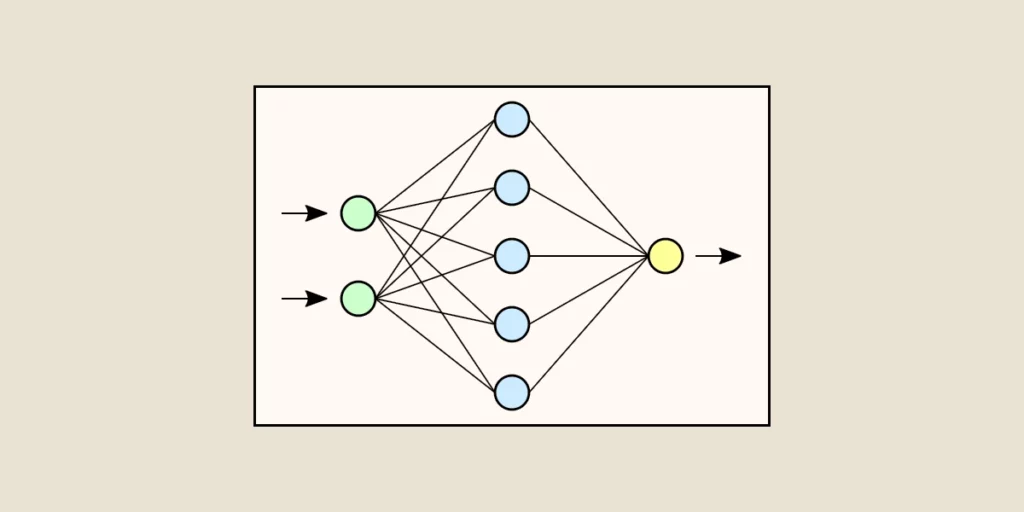
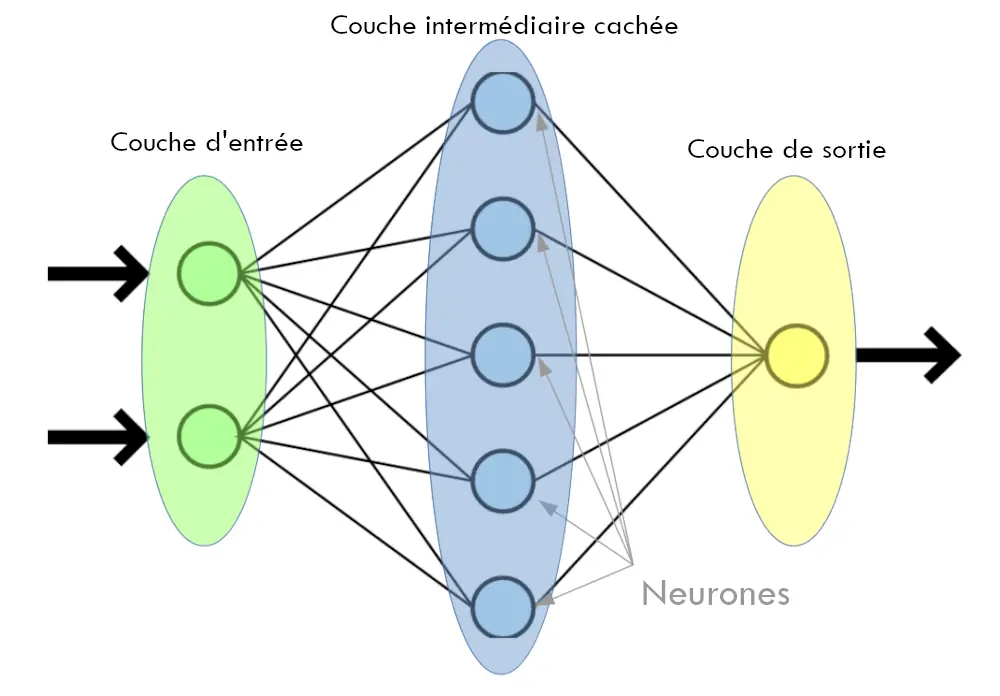
An artificial neural network learns by analyzing pre-defined examples. It is trained to develop a predictive mathematical model, such as the recognition of objects in an image. To do this, an ANN relies on numerous processors organized in layers that operate in parallel. Three types of layers are considered.
1. Input layer
This layer is where raw information is initially received. It is comparable to how optical nerves perceive an image before analyzing it.
2. Hidden intermediate layers
The raw data passes through multiple layers, each performing a partial analysis of the information before passing it to the next layer.
3. Output layer
The final layer produces the final result, representing the analyzed information.
Layer adjustment
In practice, this process can be repeated multiple times, whereby the ANN enters a learning phase where it adjusts its weights to determine the importance of each layer.
Inferences
The network can gradually make inferences, which are predictions or deductions applicable to new data.
What are the types of neural networks?
Feedforward networks
In this type of ANN, information flows in a single direction, from input to output.
Recurrent networks (RNN)
RNNs incorporate recurrent layers, enabling them to “remember” information from previous steps. This capability makes them effective for tasks such as voice recognition (they can identify words by considering previous sounds), automatic translation, and text analysis (by establishing connections between previously analyzed words).
Generative adversarial networks (GAN)
This artificial intelligence model utilizes two competing neural networks to generate realistic data.
Convolutional networks (CNN)
These networks are primarily used to process grid-structured data, such as images, making them highly effective for applications like facial recognition.
What are the concrete applications?
ANNs are at the foundation of recent immense progress in artificial intelligence and can be found in a wide array of applications.

Computer vision
Facebook’s DeepFace algorithms for facial recognition have proven to be so effective (achieving an accuracy of 97.35% in 2014) that Meta decided to suspend their use after facing several privacy controversies.
Art and creativity
Generative AIs such as Midjourney, Leonardo (for images), and Suno (for songs), along with Gen 3 by Runway (for videos), which are capable of creating works from textual descriptions, are among the most striking examples of ANN usage.
Natural language processing
Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, and Cortana are based on ANNs.
Gaming and decision-making
In 2016, AlphaGo, a tool developed by DeepMind, a subsidiary of Google, defeated the world champion of Go, a game known for its complexity and vast range of potential combinations, with a stunning score of 5 to 0. Such an achievement seemed impossible ten years earlier.
Finance
The ANN implemented by PayPal for the detection of fraudulent transactions reduced the fraud rate to 0.28% in 2024.
Automotive
Autonomous vehicles such as Waymo (also known as the Google Car) utilize ANNs (such as CNNs) for the real-time analysis of images capturing their surroundings.
Meteorology
GraphCast by Google DeepMind is capable of forecasting the weather with improved accuracy from 90% to 99.7% compared to traditional models and can provide forecasts up to 10 days in advance.