Tech companies are constantly looking for ways to improve efficiency and reduce IT costs. The concept of NoOps (No Operations) has recently entered the market as a solution for optimising deployment processes by removing traditional IT operations tasks. So what is NoOps? Why is it important? What are the key elements for its implementation? Find out in this article.
What is NoOps and why is it important?
NoOps is a concept in which IT operations are entirely automated. Developers are responsible for the design, development and deployment of applications, without any interaction with IT operations. Operations are automated and managed remotely. The ultimate goal of NoOps is to reduce deployment times and improve service reliability.
Definition of NoOps
The term NoOps is a contraction of “No Operations”. It refers to the complete automation of IT operations, including monitoring, performance management, incident resolution and resource optimisation. Development teams are responsible for designing, developing and deploying applications using automated platforms that eliminate the need for manual operations.
The benefits of NoOps for organisations
The benefits of NoOps are numerous. Firstly, the NoOps approach automates the tedious and costly tasks associated with traditional IT operations.
Operations are automated, which reduces human error and increases system reliability. What’s more, NoOps reduces deployment times, improves response times and enables greater scalability. The faster the deployment, the shorter the delivery time, so the organisation can generate revenue sooner.
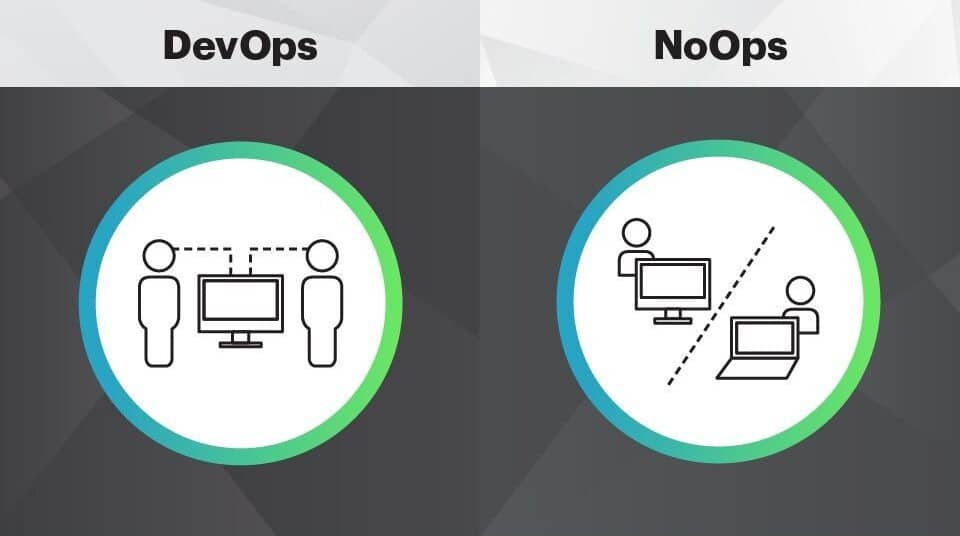
NoOps vs DevOps: the main differences
NoOps and DevOps have similar objectives, but their approach is different. DevOps focuses on automating development and operations processes to reduce deployment times and deliver better production quality. NoOps goes further by fully automating traditional IT operations such as version control, scripting or performance problem management.
The key components of NoOps
Now that you know the benefits of NoOps, discover the key processes and elements that enable operations to be automated.
Process automation
One of the key elements of NoOps is the automation of deployment processes. Automation reduces deployment times, optimises resources and increases system reliability. This is made possible in particular by native solutions made available by cloud operators.
Continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are two essential elements of NoOps. CI/CD automates the entire development process, from code through testing to production. As a result, development teams can deploy new functionalities faster and more securely.
Performance monitoring and management
Monitoring and managing application and infrastructure performance are also key components of NoOps. Automating these tasks reduces downtime and improves response times in real time.
Measuring the impact of NoOps on deployment processes
Measuring the impact of NoOps on deployment processes is crucial. Key performance indicators (KPIs) adapted to NoOps generally include :
- deployment time ;
- Deployment frequency
- failure rate ;
- service stability.
Analysing the results and monitoring these KPIs enables strategies to be adjusted accordingly. The data collected can help optimise deployment processes and improve service reliability. The feedback is clear: companies that have implemented NoOps have seen their deployment times cut, their IT costs reduced, and their systems reliability improved.
NoOps: A solution for the future?
In conclusion, NoOps is an innovative concept that aims to reduce IT costs while improving the efficiency of deployment processes. The key components of NoOps include process automation, continuous integration and deployment, and performance monitoring and management.
KPIs are a way of measuring the impact of NoOps on deployment processes and analysing the results to optimise strategies. Feedback from companies that have adopted NoOps is positive, showing an improvement in deployment time, a reduction in IT costs, and better service reliability.